Personalized Neurofeedback
for a Calmer Mind
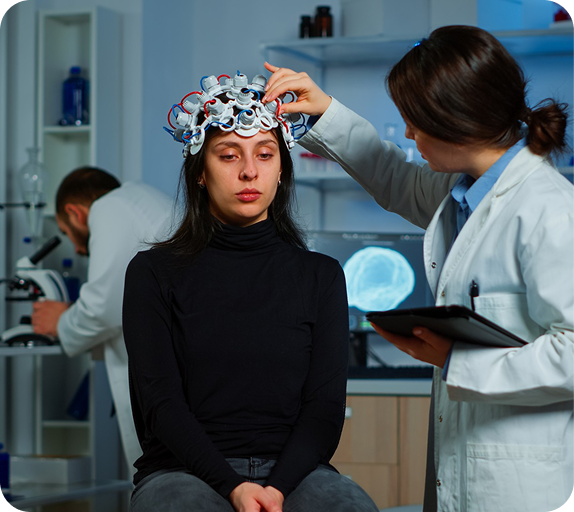
When a person struggles with attention or concentration, it may be linked to non-optimal functioning in certain brain regions or networks. Before starting Neurofeedback training, overall brain activity should be measured to identify areas or connections that may contribute to ADD/ADHD symptoms.

How It Works

For Child

For Adults

For Students

For Elders

For Child

For Adults

For Students

For Elders
What We Can Improve?
Identify Root Causes

Personalized Brain Insights


Neurofeedback Training

Trackable, Lasting Progress
What Happens
at the Brain Level in ADHD
Frontal Lobes

Sustained Attention Network
Divided Attention Network
Divided Attention Network
What we train with Neurofeedback

Results that can be observed

Improvements in concentration
Greater ability to maintain focus and complete tasks with fewer distractions.

Better reading comprehension
Enhanced understanding and retention of written information.

A larger capacity for organization
Improved skills in planning, prioritizing, and managing responsibilities efficiently.
Level 5
intervention for ADHD
Neurofeedback is now ranked as a Level 5 intervention. The highest level of effectiveness according to the “Evidence-based Practice in Neurofeedback and Biofeedback 2023” reference guide.
It has been shown that the benefits obtained with Neurofeedback are usually long-lasting and even that optimized brain capabilities continue to improve in the months following the end of Neurofeedback trainings.

What are the
symptoms of ADHD?
This mental health disorder can take three distinct forms. ADHD is the predominantly inattentive type of attention deficit disorder. It is characterized by an excessive tendency to be distracted, such as significant slowness during the execution of intellectual or routine tasks.
ADHD is a predominantly hyperactive-impulsive type of ADHD characterized by high motor or mental agitation and/or disproportionate impulsivity. It also includes a lack of inhibition. ADHD is a type of attention deficit disorder present in both adults and children. It is characterized by inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity. ADHD is said to be the most common form among North American school-aged children.
ADHD can manifest in several ways:
- hyperactivity,
- problems with concentration,
- attention deficit,
- problems with planning and organization,
- impulsivity and mental (incessant and rapid flow of thoughts) or physical (fidgeting) agitation.
Diagnostic Evaluation of ADHD
Diagnosing ADHD is not straightforward, and there is no medical test that can accurately do so. The healthcare professional, notably the neuropsychologist, who diagnoses ADHD conducts a comprehensive evaluation of the child and their environment. This specialist may consider several elements:
- the child’s development since birth,
- their behavior at home, school, and elsewhere,
- their symptoms (intensity and duration),
- and their difficulties at school or in task execution.
To determine if a child has ADHD, the neuropsychologist or other qualified professional may use behavioral criteria developed by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition, as well as psychometric tools. Psychological and neuropsychological tests can also help diagnose ADHD.

FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
The difference between the two is that ADD is a condition involving only attention difficulties without the presence of physical and mental hyperactivity. In contrast, ADHD is attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Children with ADHD are generally perceived as individuals who are bursting with energy, fidgety, and intense or impulsive.
The difference between the two is that ADD is a condition involving only attention difficulties without the presence of physical and mental hyperactivity. In contrast, ADHD is attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Children with ADHD are generally perceived as individuals who are bursting with energy, fidgety, and intense or impulsive.
The difference between the two is that ADD is a condition involving only attention difficulties without the presence of physical and mental hyperactivity. In contrast, ADHD is attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Children with ADHD are generally perceived as individuals who are bursting with energy, fidgety, and intense or impulsive.
The difference between the two is that ADD is a condition involving only attention difficulties without the presence of physical and mental hyperactivity. In contrast, ADHD is attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Children with ADHD are generally perceived as individuals who are bursting with energy, fidgety, and intense or impulsive.

Not Sure Where to Start?
available. Book your FREE phone consultation today.
